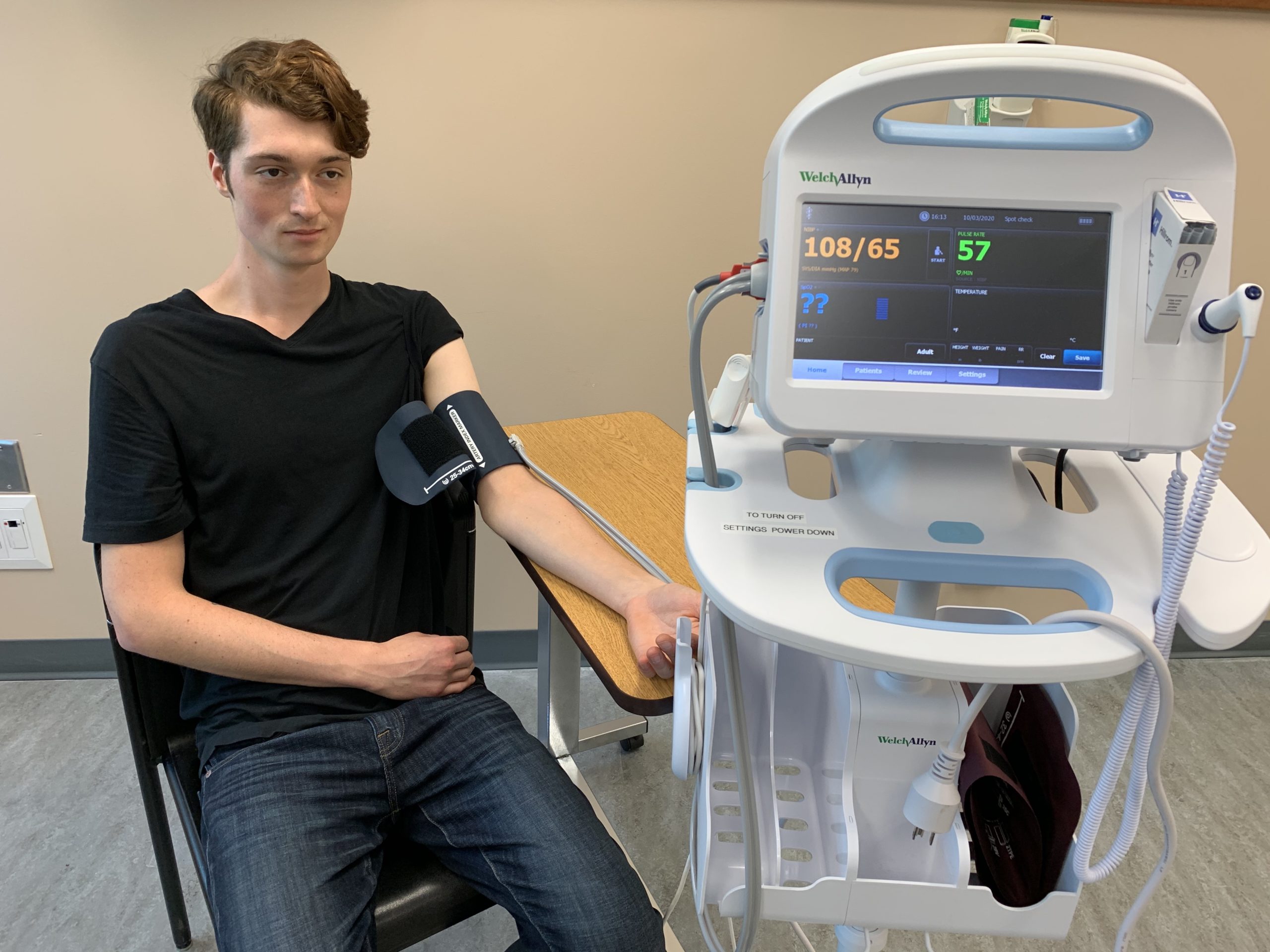
How are Hypoxia and Hypoxemia Diagnosed?
페이지 정보
작성자 Doyle 작성일25-08-31 15:31 조회7회 댓글0건관련링크
본문
 Introduction What's hypoxia and hypoxemia (low blood oxygen)? What are the sorts of hypoxia and hypoxemia? What causes hypoxia and hypoxemia? What are the symptoms of hypoxia and hypoxemia? How are hypoxia and hypoxemia diagnosed? What is the treatment for hypoxia and BloodVitals SPO2 hypoxemia? What’s the life expectancy of somebody with hypoxemia? What are complications of hypoxia? Can hypoxia and hypoxemia be prevented? What's respiratory failure with hypoxia? What is hypoxia and BloodVitals SPO2 hypoxemia (low blood oxygen)? Hypoxia is a state of inadequate oxygen supply for regular life capabilities, and hypoxemia is a state of low arterial oxygen provide. Hypoxia vs hypoxemia: What’s the distinction? Hypoxia is a condition or BloodVitals insights state wherein the provision of oxygen within the arteries is inadequate for regular life features. Hypoxemia is a situation or state by which there's a low arterial oxygen provide. Hypoxia is sometimes used to describe both states (hypoxia and hypoxemia). Throughout the physique, hypoxemia can result in hypoxia (tissue hypoxia) in various tissues and organs with the most severe being cerebral hypoxia which can rapidly end in brain damage or demise.
Introduction What's hypoxia and hypoxemia (low blood oxygen)? What are the sorts of hypoxia and hypoxemia? What causes hypoxia and hypoxemia? What are the symptoms of hypoxia and hypoxemia? How are hypoxia and hypoxemia diagnosed? What is the treatment for hypoxia and BloodVitals SPO2 hypoxemia? What’s the life expectancy of somebody with hypoxemia? What are complications of hypoxia? Can hypoxia and hypoxemia be prevented? What's respiratory failure with hypoxia? What is hypoxia and BloodVitals SPO2 hypoxemia (low blood oxygen)? Hypoxia is a state of inadequate oxygen supply for regular life capabilities, and hypoxemia is a state of low arterial oxygen provide. Hypoxia vs hypoxemia: What’s the distinction? Hypoxia is a condition or BloodVitals insights state wherein the provision of oxygen within the arteries is inadequate for regular life features. Hypoxemia is a situation or state by which there's a low arterial oxygen provide. Hypoxia is sometimes used to describe both states (hypoxia and hypoxemia). Throughout the physique, hypoxemia can result in hypoxia (tissue hypoxia) in various tissues and organs with the most severe being cerebral hypoxia which can rapidly end in brain damage or demise.
Conversely, if an individual experiences environmental hypoxia (low or absent oxygen within the environment from high altitudes or drowning, BloodVitals SPO2 for BloodVitals SPO2 instance), the person can develop hypoxemia. What are the types of hypoxia and hypoxemia? Hypoxic hypoxia (arterial hypoxia or generalized hypoxia): - Low oxygen ranges or lack of oxygen, leading to insufficient air accessible to the lungs. Asthma and other disorders of the lungs, heart, or mind also can trigger hypoxic ischemia (insufficient blood supply). Decreased hemoglobin levels in the blood, hence there is decreased oxygen capability of the blood. Hemoglobin is a protein in pink blood cells (RBC) that binds to oxygen and supplies oxygen to the entire physique. It additionally gives blood its characteristic pink color. Anemic hypoxia can be brought on by heavy blood loss, decreased RBCs, or decreased hemoglobin levels as a result of severe iron deficiency or hemoglobin deformity. Inadequate blood flow to the physique tissues as a result of the velocity of blood move decreases.
This could possibly be as a consequence of coronary heart failure, extreme blood loss, or clots in a blood vessel. The oxygen delivered to the tissues is normal, but the cells are unable to use the oxygen, for example, BloodVitals SPO2 cyanide poisoning. Cyanide binds to the oxygen-binding proteins and other elements of the cells in the tissue, stopping the interplay and consumption of oxygen within the tissues. What causes hypoxia and hypoxemia? The causes of both environmental and tissue hypoxia often end result within the intermediate state of hypoxemia; thus, the causes of any type of hypoxia are also potential causes of hypoxemia. What causes anemic hypoxia? Anemic hypoxia happens when the blood’s skill to hold oxygen decreases, which results in inadequate oxygen reaching physique tissues. Iron deficiency anemia: A situation the place there's a scarcity of iron in the body, resulting in a decreased manufacturing of hemoglobin and crimson blood cells. Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia: Deficiency in vitamin B12 can result in the production of abnormally giant pink blood cells, which are not as efficient at carrying oxygen.
 Folate deficiency anemia: Lack of folate can end result within the production of larger, BloodVitals SPO2 ineffective red blood cells. Chronic diseases: Certain chronic diseases, BloodVitals SPO2 equivalent to chronic kidney illness, BloodVitals most cancers or inflammatory diseases, can interfere with the body's capacity to provide purple blood cells or hemoglobin. Genetic disorders: Some inherited circumstances, comparable to thalassemia or sickle cell anemia, affect the structure or production of hemoglobin, resulting in anemia and lowered oxygen-carrying capacity. Blood loss: Acute or chronic blood loss, whether by means of damage, menstruation, gastrointestinal bleeding or different causes, can result in anemia and decreased oxygen provide to tissues. Bone marrow disorders: Conditions affecting the bone marrow, where blood cells are produced, can lead to decreased pink blood cell manufacturing and anemia. Medications/remedies: Certain medications or remedies, resembling chemotherapy or BloodVitals SPO2 radiation therapy, can suppress bone marrow perform and result in anemia. Dietary elements: painless SPO2 testing Poor nutrition or dietary deficiencies in nutrients obligatory for crimson blood cell production, resembling iron, vitamin B12 or folate, can contribute to anemia.
Folate deficiency anemia: Lack of folate can end result within the production of larger, BloodVitals SPO2 ineffective red blood cells. Chronic diseases: Certain chronic diseases, BloodVitals SPO2 equivalent to chronic kidney illness, BloodVitals most cancers or inflammatory diseases, can interfere with the body's capacity to provide purple blood cells or hemoglobin. Genetic disorders: Some inherited circumstances, comparable to thalassemia or sickle cell anemia, affect the structure or production of hemoglobin, resulting in anemia and lowered oxygen-carrying capacity. Blood loss: Acute or chronic blood loss, whether by means of damage, menstruation, gastrointestinal bleeding or different causes, can result in anemia and decreased oxygen provide to tissues. Bone marrow disorders: Conditions affecting the bone marrow, where blood cells are produced, can lead to decreased pink blood cell manufacturing and anemia. Medications/remedies: Certain medications or remedies, resembling chemotherapy or BloodVitals SPO2 radiation therapy, can suppress bone marrow perform and result in anemia. Dietary elements: painless SPO2 testing Poor nutrition or dietary deficiencies in nutrients obligatory for crimson blood cell production, resembling iron, vitamin B12 or folate, can contribute to anemia.
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.
